Why is data security important ?
1467 Views |
Data loss prevention (DLP) is a part of a company’s overall security strategy that focuses on detecting and preventing the loss, leakage or misuse of data through breaches, ex-filtration transmissions and unauthorized use.
DLP is also a way for companies to classify business critical information and ensure the company’s data policies comply with relevant regulations, such as HIPAA, GDPR and PCI-DSS. A properly designed and configured DLP solution streamlines reporting to meet these compliance and auditing requirements.
Finally, some DLP solutions can also provide alerts, enable encryption and isolate data when a breach or other security incident is detected. In doing so, the DLP solution can expedite incident response by identifying areas of weakness and anomalous activity during routine networking monitoring.
A DLP solution makes use of a combination of standard cybersecurity measures, such as firewalls, endpoint protection tools, monitoring services and antivirus software, and advanced solutions, such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML) and automation, to prevent data breaches, detect anomalous activity and contextualize activity for the infosec team.
DLP technologies typically support one or more of the following cybersecurity activities:
- Prevention: Establish a real-time review of data streams and immediately restrict suspicious activity or unauthorized users
- Detection: Quickly identify anomalous activity through improved data visibility and enhanced data monitoring measures
- Response: Streamline incident response activities by tracking and reporting data access and movement across the enterprise
- Analysis: Contextualize high-risk activity or behavior for security teams to strengthen prevention measures or inform remediation activities
A DLP solution protects sensitive data by helping the company:
- Improve adherence to existing security policies by quickly
- Meet complex and evolving compliance standards by classifying and storing sensitive, confidential, proprietary or other business-critical data in a flexible and adaptable way
- Improve data visibility across the entire network and all endpoints through a 360-degree view of the enterprise
- Reduce financial risk associated with data loss or leaks, especially as it relates to ransomware attacks
- Decrease the chance of reputational harm by preventing data breaches and/or quickly identifying security incidents so as to minimize the impact of such an event
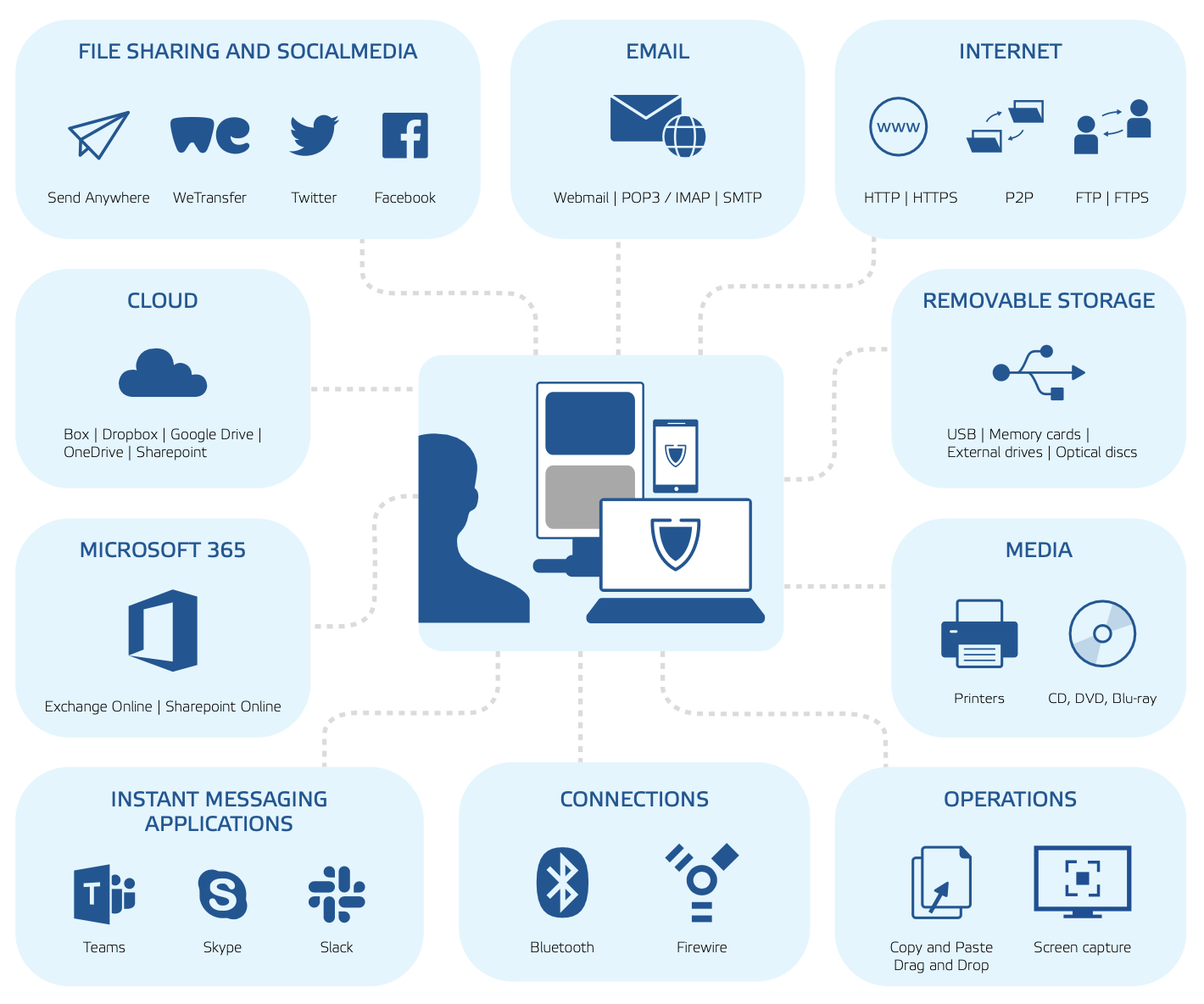
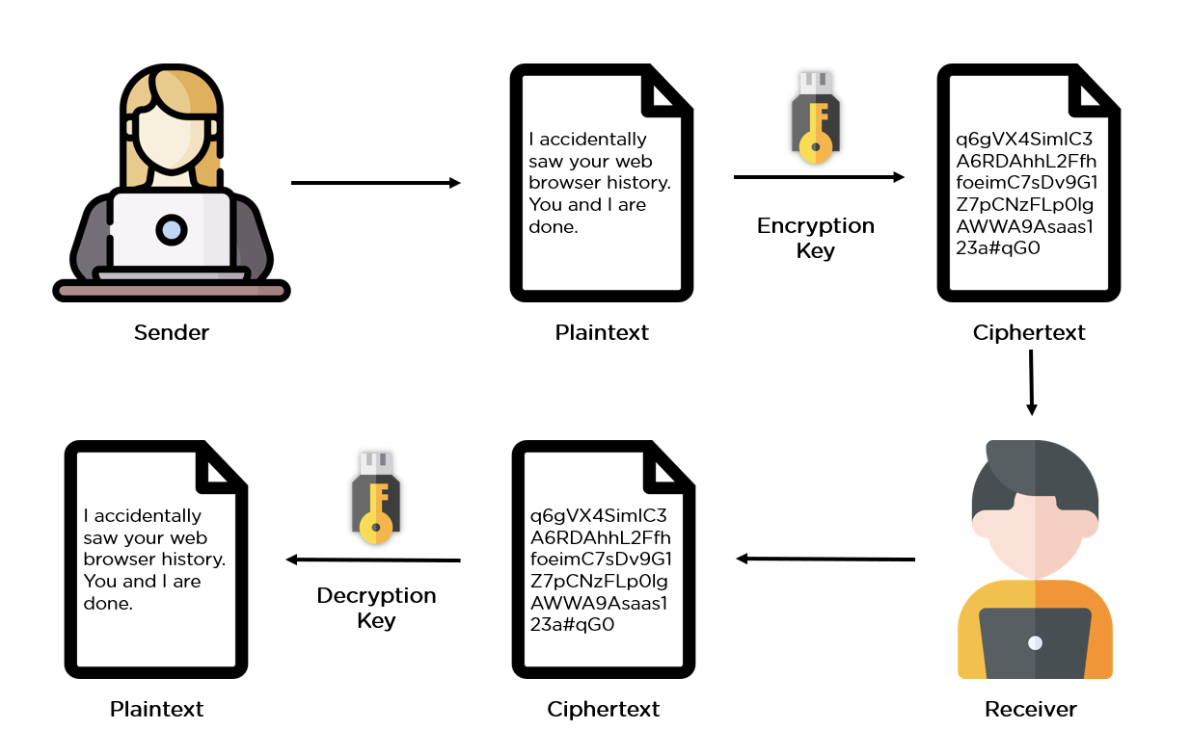
Data Encryption - Encryption in cyber security is the conversion of data from a readable format into an encoded format. Encrypted data can only be read or processed after it's been decrypted.
If anyone wonders why organizations need to practice encryption, keep these four reasons in mind:
- Authentication: Public key encryption proves that a website's origin server owns the private key and thus was legitimately assigned an SSL certificate. In a world where so many fraudulent websites exist, this is an important feature.
- Privacy: Encryption guarantees that no one can read messages or access data except the legitimate recipient or data owner. This measure prevents cybercriminals, hackers, internet service providers, spammers, and even government institutions from accessing and reading personal data.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industries and government departments have rules in place that require organizations that work with users’ personal information to keep that data encrypted. A sampling of regulatory and compliance standards that enforce encryption include HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and the GDPR.
- Security: Encryption helps protect information from data breaches, whether the data is at rest or in transit. For example, even if a corporate-owned device is misplaced or stolen, the data stored on it will most likely be secure if the hard drive is properly encrypted. Encryption also helps protect data against malicious activities like man-in-the-middle attacks, and lets parties communicate without the fear of data leaks.
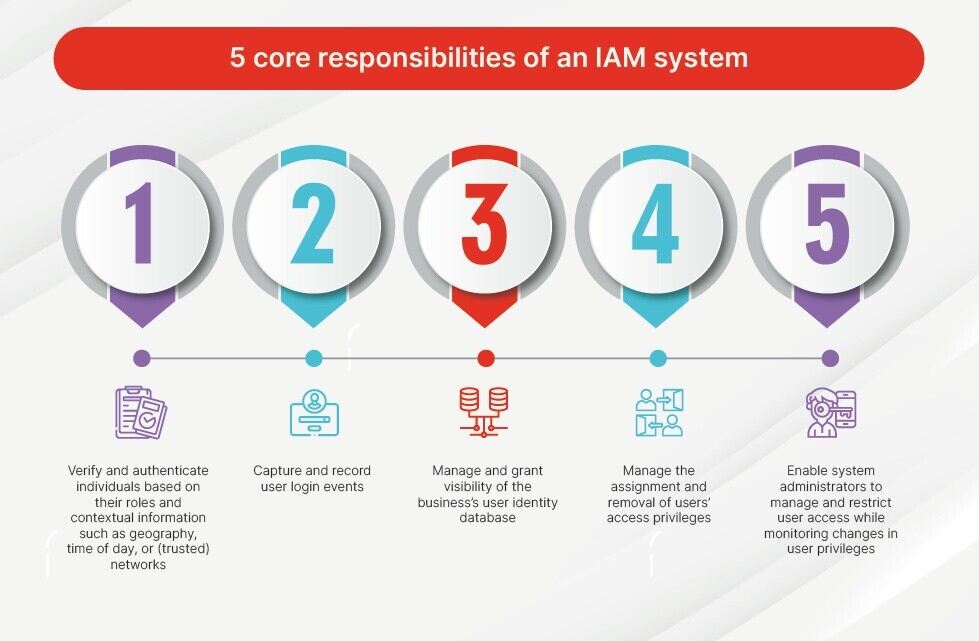
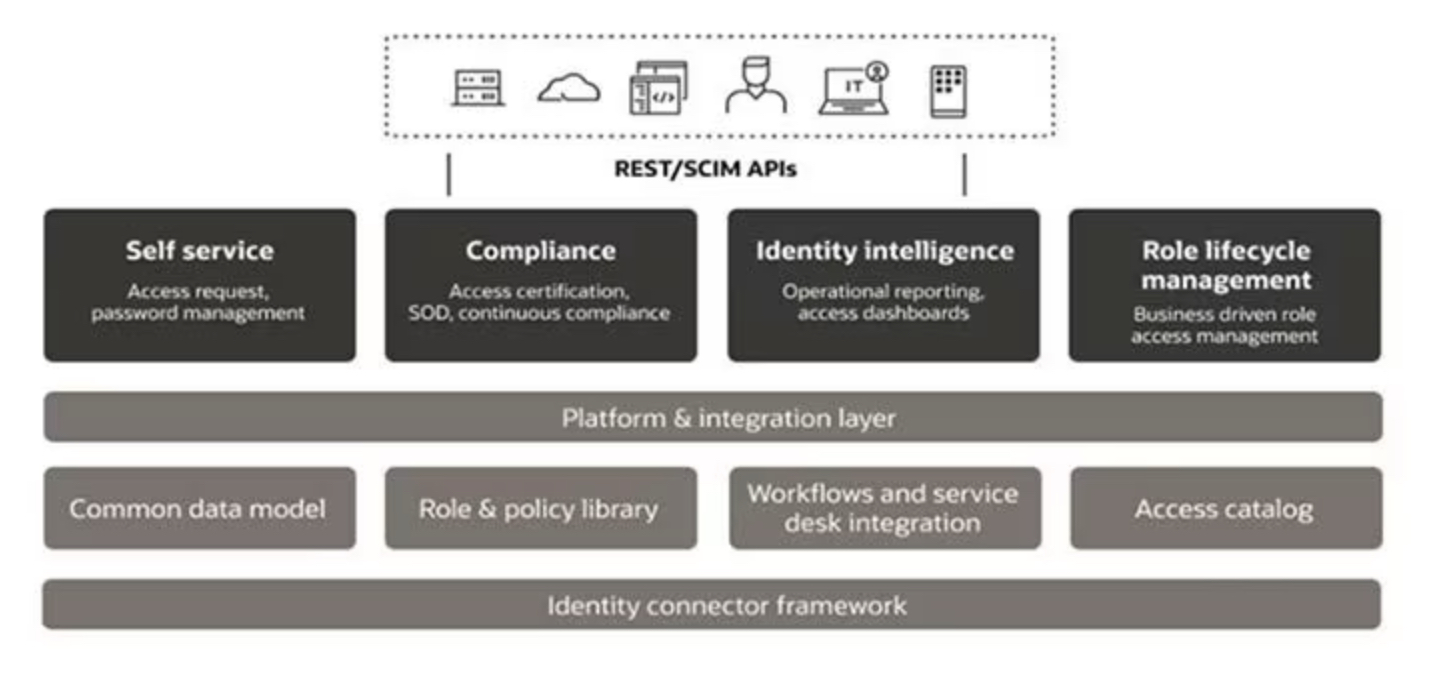
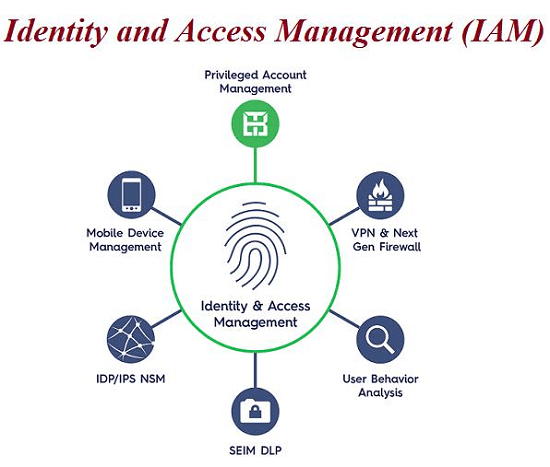
Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a framework of policies, processes, and technologies that enable organizations to manage digital identities and control user access to critical corporate information. By assigning users with specific roles and ensuring they have the right level of access to corporate resources and networks, IAM improves security and user experience, enables better business outcomes, and increases the viability of mobile and remote working and cloud adoption.
Compromised user credentials are among the most common targets for hackers to gain entry into organizations’ networks through malware, phishing, and ransomware attacks. It is therefore vital for enterprises to safeguard their most valuable resources. Many are increasingly turning to Identity and Access Management (IAM) technology to protect their data and people.
The core responsibilities of an IAM system are to:
- Verify and authenticate individuals based on their roles and contextual information such as geography, time of day, or (trusted) networks
- Capture and record user login events
- Manage and grant visibility of the business’s user identity database
- Manage the assignment and removal of users’ access privileges
- Enable system administrators to manage and restrict user access while monitoring changes in user privileges
Implementing an Identity Management system provides a wide range of benefits to organizations, such as:
- Secure access: Opening networks to more employees, new contractors, customers, and partners offers greater efficiency and productivity, but it also increases the risk. An IAM solution enables businesses to extend access to their apps, networks, and systems on-premises and in the cloud without compromising security.
- Reduced help desk requests: An IAM solution removes the need for users to submit password resets and help desk requests by automating them. This enables users to quickly and easily verify their identity without bothering system admins, who in turn are able to focus on tasks that add greater business value.
- Reduced risk: Greater user access control means reduced risk of internal and external data breaches. This is vital as hackers increasingly target user credentials as a key method for gaining access to corporate networks and resources.
- Meeting compliance: An effective IAM system helps a business meet their compliance needs amid a landscape of increasingly stringent data and privacy regulations
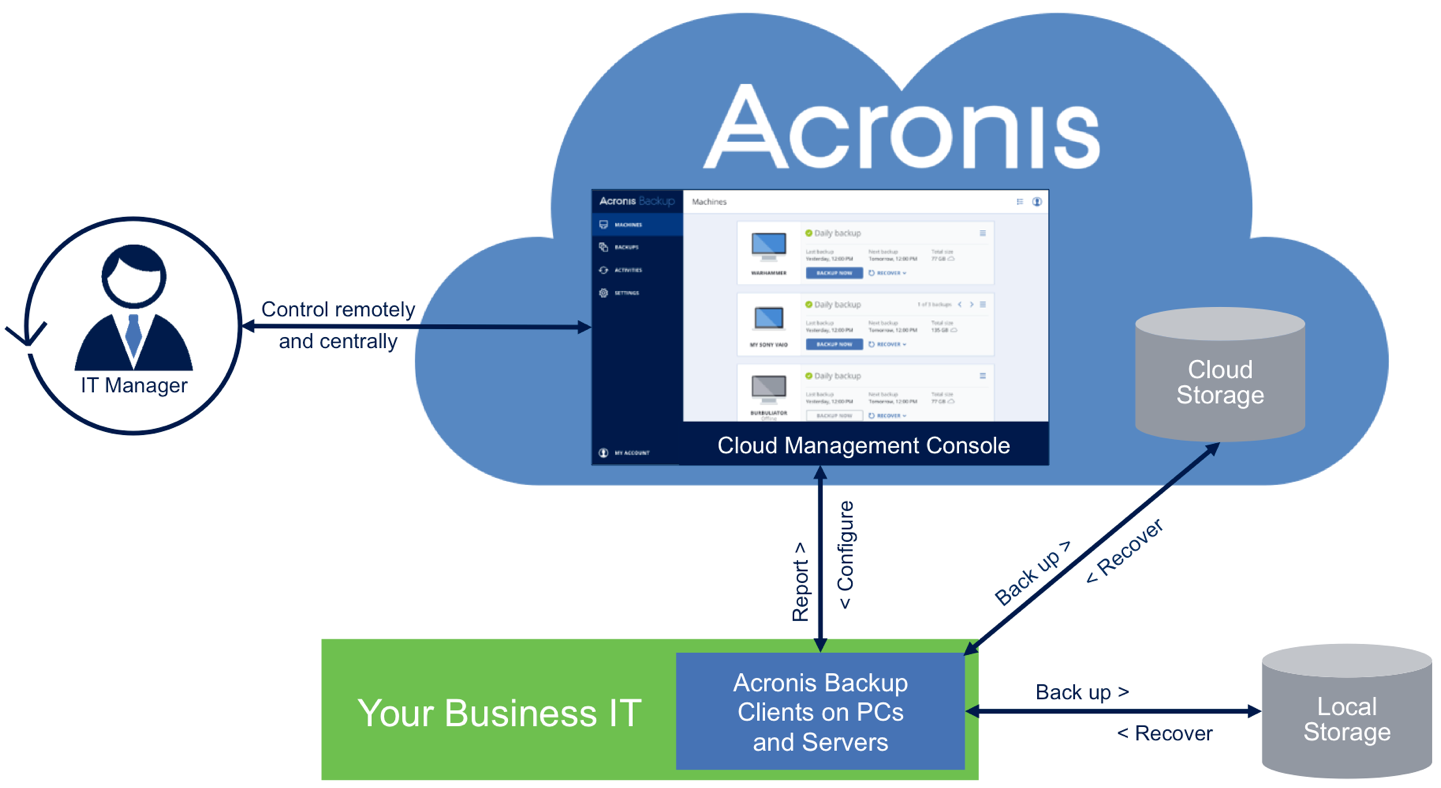
Data Backup is the process of making a copy of your digitized data and other business information in case your data is damaged, deleted or lost. The backup copy is then used to recover or restore your data for business continuity and disaster recovery. Many IT organizations make multiple backup copies and keep one copy on-premises for the fastest recovery and keep a second copy offsite or in the cloud in case their on-prem copy is damaged, typically due to natural or man-made disaster.
อ้างอิงข้อมูล
Data loss prevention (DLP)
https://www.forcepoint.com/product/dlp-data-loss-prevention
https://www.safetica.com
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
https://www.fortinet.com/resources/cyberglossary/identity-and-access-management
https://www.sentinelone.com/platform/singularity-identity/
https://www.crowdstrike.com/products/identity-protection/
https://www.xcitium.com/mdr/access-and-identity-management/



